Cliggett’s Intent and Purpose in Writing Grains from Grass
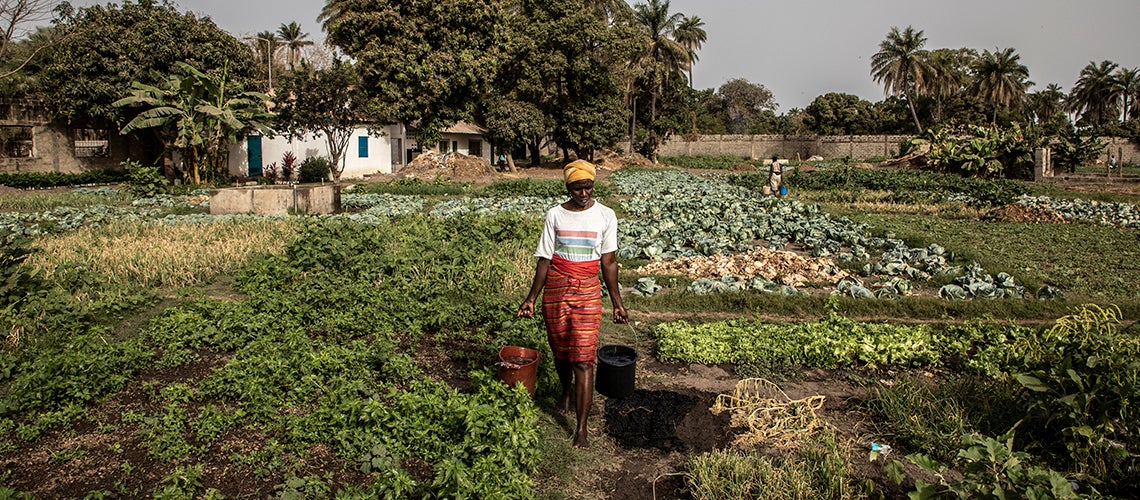
Lisa Cliggett’s Grains from Grass (2005) studies the Tonga people of the Gwembe Valley in Southern Zambia. Her findings can speak to Western readers who are disillusioned with the individualism of their own societies. This disappointment motivates many Westerners to search for cultures that still honor the sacredness of the family (p. 1). But Cliggett disabuses Western readers of such a stereotype in her study of the Tonga people. In this community, diverse systems of collaboration, generosity, and charity exist based not primarily on “moral duty or altruistic sentiments” but on “necessity in the face of limited choices”. Of particular interest to this research is the relevance of gender-specific survival modes. Cliggett explores family dynamics related to survival in economically vulnerable communities. She discovers the significance of kinship networks for combating poverty and injustice. Cliggett’s understanding of vulnerability considers differences in access and control of resources among different members of Tonga society. Her findings correct simplistic notions regarding impoverished nations, let alone a continent such as Africa (Cliggett, 2005, p. 2-19).
Cliggett (2005) investigates the ways that older women and men in the Gwembe Valley interact with a relational world acutely affected by scarcity of resources (p. 22). And this research explores the ways family and community provide for or ignore the needs of elderly women and men in ways not obvious to an outside observer. The purpose of such analysis is to correct oversimplified visions of social problems in Africa on the one hand, as well as ingenuous ideas of the noble altruism of African families. It is argued that care for the elderly needy is not a natural phenomenon to any human society whether industrialized and modern or agricultural and traditional. A more nuanced vision of the multifaceted process of decision making in relation to helping needy family members is needed. This helps societies worldwide to be wiser about the connection between family relationships, poverty, and globalization. Thus, Cliggett addresses naïve Western notions of former times and other places where the support of family members simply flowed out of the goodness of human nature. Caring for the elderly is not a “natural” component of non-industrialized societies, which begs the question, “Where can we find positive examples of this behavior?” Cliggett’s aim to identify differences – “gender, class, generational or historical” – amidst generalizations about “poor and disaster prone” peoples, yields a more comprehensive view of our world’s complex reality. The result is a framework that ties together the agency of the individual, kinship economic models, and long-term analysis of at-risk populations. Cliggett (2005) hopes this will produce theoretical concepts which give “broader meaning” to the phenomena social science research observes in vulnerable communities (Cliggett, 2005, p. 22-75).
The Resource Bases of Elderly Tonga Women and their Strategies to Access Them
Cliggett (2005) gives a general description of Gewmbe villagers’ economic situation as consisting of resource ownership, small entrepreneurialism, government assistance, and wage employment (p. 80). In times of economic adversity all these factors are used by individuals in ways that reflect their gender, age, social networks, and the “capacity to negotiate relationships” for survival (p. 80).
Cliggett (2005) found that women made the adjustment to old age with less disruption, and even with positive expectations regarding its potential benefits. Tonga society practices matrilineal kinship in which primary family identity is shared between women and their children (p. 20). Perhaps surprisingly, in this system widowhood or divorce can give women new freedom to work autonomously, or preferably to be supported from the households of their adult children. Thus, elderly women’s means of survival are connected to their maternal identity in relation to the children they spent their lives sacrificing for and serving. Matrilineal kinship strongly influences how the Tonga people strategize for obtaining resources. But this social system is not tidy, rather, individuals must make compromises and bargain creatively (Cliggett, 2005, p. 19-20).
Women have been excluded from significant sources of sustenance and have therefore formed innovative means for self-perseveration in old age (Cliggett, 2015, p. 64). Women have less access than men to resources that can be used to generate income, but the former employ diverse types of “craft and service-oriented skills”. The primary way elderly Gwembe women provide for themselves is developing social networks from which they can receive food and other goods. As Gwembe women advance in age, they hope these strategically built relationships can help them procure food, housing, service, and general needs. The most precarious situation for an elderly woman is if she has no close adult male kin who can provide help (Cliggett, 2015, p. 83-108).
The Resource Bases of Elderly Tonga Men and their Strategies to Access Them
Tonga men tend to hold on to their position of social power as they age and cannot work the fields and care for themselves (Cliggett, 2015, p. 19). As stated earlier, matrilineal kinship means fathers do not share primary family identity with their children. In this family model, elderly men mitigate against disenfranchisement by exerting their right to adult son’s labor and through bride price, the amount paid for daughters. Despite men’s lack of shared clan identity with wives and children, they do have kinship roles giving them control over resources at the level of the nuclear family. Thus, men’s relationships with their offspring are largely based on formal rights. Women’s relationship with their adult children, on the other hand, depends on connection through kinship and the ties of the “mother-child experience”. By the time they become elderly, men have generally been able to accumulate an amount of wealth which can be used to support themselves. And in a polygamous society, an elderly man is likely to have at least one living wife residing in his home who can care for him (Cliggett, 2015, p. 20-38).
Tonga men are more able than women to clear new bush fields and a man’s inheritance is traditionally passed on to male heirs. Therefore, predominant male ownership of land has been perpetuated over several generations (Cliggett, 2015, p. 65). Cash-producing activities that men have access to include selling agricultural tools they make, milk from cattle, and garden produce. Men can also offer their services in home construction, brickmaking, and other forms of manual labor. By the time a man is older, one reason his need for such forms of small income decreases is because of accumulated resources. A second reason is that a man’s dependents, such as daughters soon to marry and sons with incomes of their own, will provide additional resources. It is through residential arrangements with extended family members that most elderly men receive the bulk of their food and have their basic needs met (Cliggett, 2015, p. 83-97).
The idea of a father receiving and “income” from his adult children seems strange to a Westerner like me who prizes independence and would see a parent being supported in such a way as a sign of failing to achieve independence. But from a Zambian perspective, such an arrangement can be seen as a form of retirement at the end of a life lived in significant part to supporting offspring.
How Such Strategies Relate to Elderly Men and Women’s Connections to the “Ritual World”
In Africa, roughly a century of European slave trade followed by a century of industrialization and colonization have deeply affected “social, economic, and belief systems” (Cliggett, 2015, p. 53). In Zambia, differences in how global economic vulnerability has affected different regions produced richer and poorer regions. Seasonal fluctuation of food availability has led to agricultural migration, profoundly altering people’s connection to their land. This in turn has undermined the importance of ritual institutions and their leaders, elderly men (Cliggett, 2015, p. 56-62).
The funeral homestead is a “market of sorts” where people exchange and sell as well as singing funeral songs and developing relational networks, i.e. catching up on local gossip and current events (Cliggett, 2015, p. 82). Thus, a wide range of goods could be found by villagers and visitors at these recurring rural markets. Women’s participation in religious funeral rights is fundamental in the form of food preparation. The preparation of food is empowering to women, in fact the funeral period officially ends when the women finish clearing out the fire ovens (Cliggett, 2-15, p. 82-121).
Christianity has grown in the Gwembe valley, but the elderly population is not a significant presence in church life (Cliggett, 2015, p. 117). I wonder if elderly men and women do not see as much of the benefits of Christianity as a theology and community versus the younger more entrepreneurial population. The Pentecostal type of Christianity that has been so influential in Africa is highly individualistic, emphasizing God’s intervention in the life of the individual, the potential to receive his blessing on finances and health. Perhaps the elderly see this as not contributing to the traditional cultural and social institutions that benefit them, or worse, perhaps they see them as threatening. Ancestor worship is a traditional part of indigenous Tonga religious practice, and I am curious how different Christian denominations have interacted with this practice.
Men are seen as having agency regarding the spirit world in a direct way while women are beset upon by spirits, at times harmlessly but in some cases dangerously (Cliggett, 2015, p. 132). Women can use the cultural belief that they are vulnerable to possession by evil spirits as a means for requesting help (p. 140). A situation of spiritual attack makes an elderly woman victim a sympathetic plight for members of her kinship network.
Some Effects of Migration on Traditional Kinship Support Paradigms
Economic pressures and opportunities lead many of the Tonga people to migrate away from their home villages. But connections with family back home are generally maintained, not through remittances but sporadic gifts. Such contributions would not amount to a reliable or significant source of income (Cliggett, 2015, p. 148). And for those who migrate, making their new lives work is the main priority. The imposition of requests for help from visitors from a migrant’s home village makes greater distance helpful. The farther migrants move away, the more of a “buffer from such impositions” exists. The best way a visitor from back home can obtain a gift from a prosperous migrant relative is to make the request in person. Often the gift request is attended to, and sometimes at significant cost to the giver. But the gift is based on the nature of the interaction and is not a given, therefore the person requesting goes to great efforts to be gracious and diplomatic. Such gifts do not amount to a reliable source of income for villagers who remain back home. At best these contributions are a helpful part of a village’s economic system, but not a main source. If a migrant does not maintain ties with his or her home village, there is also a downside. This will result in being cut off from social ties to the home village and material, emotional, and spiritual benefits it can offer (Cliggett, 2015, p. 152-5).
Conclusion
Cliggett (2005) makes a compelling argument that simplistic stereotypes of the drama and needs of the African people result in misguided endeavors to save victims and solve problems without tackling foundational causes (p. 48). The “framework of vulnerability” approach rightly advocates for multifaceted research on issues such as environmental crises, access to food, and kinship. This approach mitigates against tendencies in the social sciences to generalize about the circumstances of all members of a village, region, or nation (p. 49). I agree with the notion that at-risk populations’ foundational problem is relational. And each member of a family negotiates for resources within the kinship network with differing “desires, abilities, and power” (p. 50).
I understand the need to find out who copes better or worse among vulnerable populations. First, those who cope poorly can learn from those who have innovated, negotiated, strategized, and succeeded. Second, I appreciate the importance of determining what unjust phenomena may be creating situations of inequality of coping. Thirdly, it is vital simply to determine who the poorest copers are to target them as those in greatest need.
Cliggett’s work demonstrates that support is channeled through “continually negotiated social networks” in different ways by elderly men and women (p, 158). With the participation of multiple family members in the chain of resources, a decision or failure to perform by any individual threatens the entire system. Cliggett (2004) demonstrates how individual’s in the Gwembe valley are able not only to survive but to prosper (p. 167). This account of individual human agency in poor communities emphasizes the endeavor to progress and flourish contra the caricature of acquiescence and acceptance of poverty. Cliggett’s work effectively counters the error of overly attributing worldview – how people think in sweeping generic national-ethnic terms – instead of observing reality of experience and agency on the ground (p. 167). I agree with the general position of this work as it posits that the most simple and foundational method of combatting the reductive tendency towards sociocultural analysis is the place the target community in “center stage” (p. 168), rather than giving too much credence to stereotypes and generalizations about vulnerable peoples such as the Tonga of the Gwembe valley.
References
Cliggett, L. (2005). Grains from grass: Aging, gender, and famine in rural Africa. Cornell University Press.